Intro to Permguard
What is Permguard?
Permguard is a distributed authorization platform designed to implement a modern authorization protocol based on Zero Trust principles.
Its core purpose is to define who is allowed to perform which actions on which resources, producing clear and verifiable authorization decisions.
Permguard models authorization through a unified policy framework:
- Who — identities such as users or workloads
- Can Access — permissions granted through policies
- Which Resources — the protected resources or operations
This model provides a consistent and extensible foundation for enforcing fine-grained access control across distributed systems.
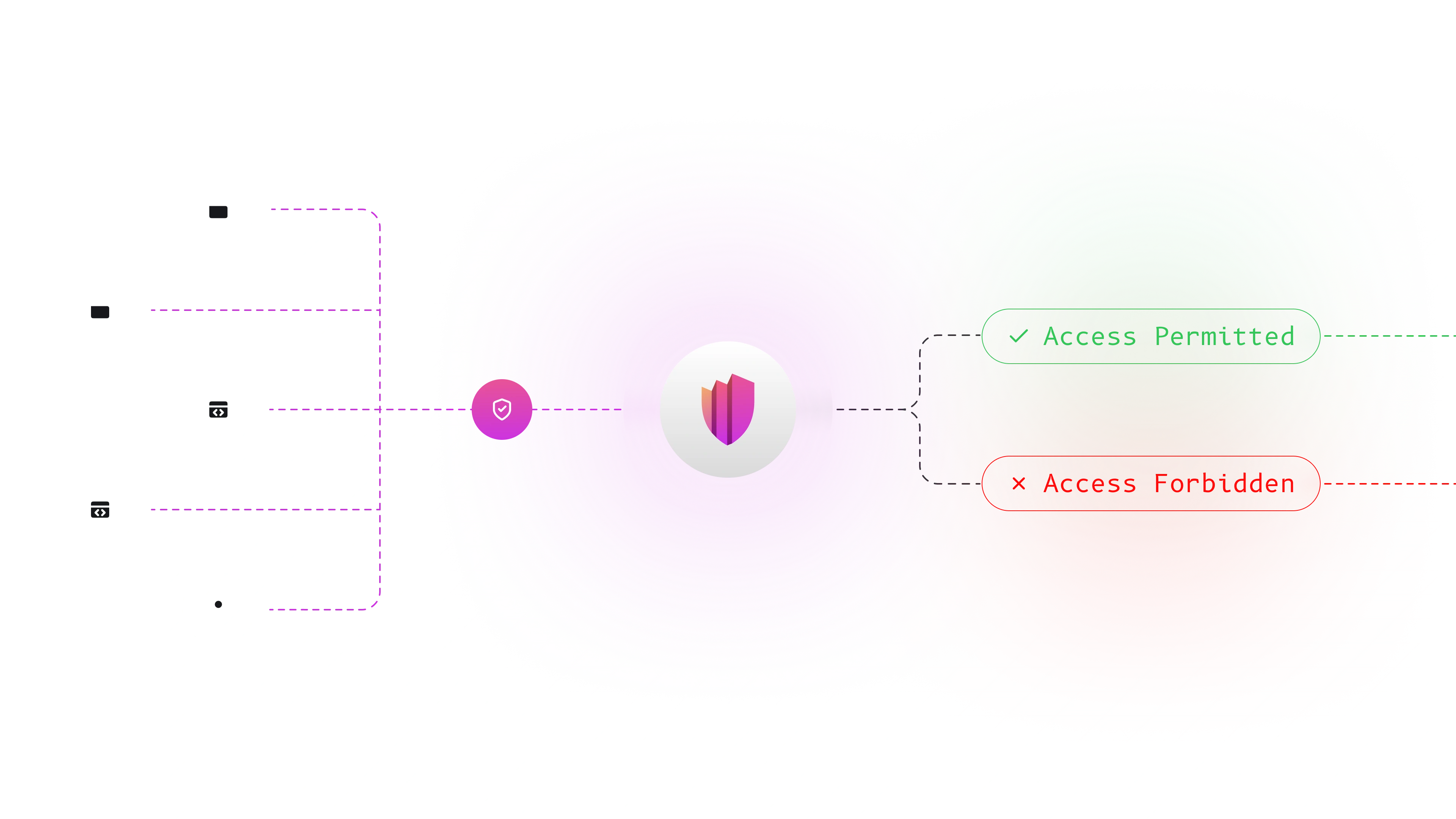
What Permguard Enforces
The fundamental Zero Trust rule in Permguard is simple: every incoming request must be validated before the application processes it.
This applies uniformly across all interaction types — synchronous APIs, asynchronous messages, event streams, WebSocket frames, and cross-service calls — ensuring consistent enforcement at both the network layer and the application layer.
Beyond the input boundary, Permguard also governs in-code authorization policies, allowing applications to perform fine-grained checks at critical points:
- before calling a domain service
- before executing a sensitive command
- before accessing or mutating data
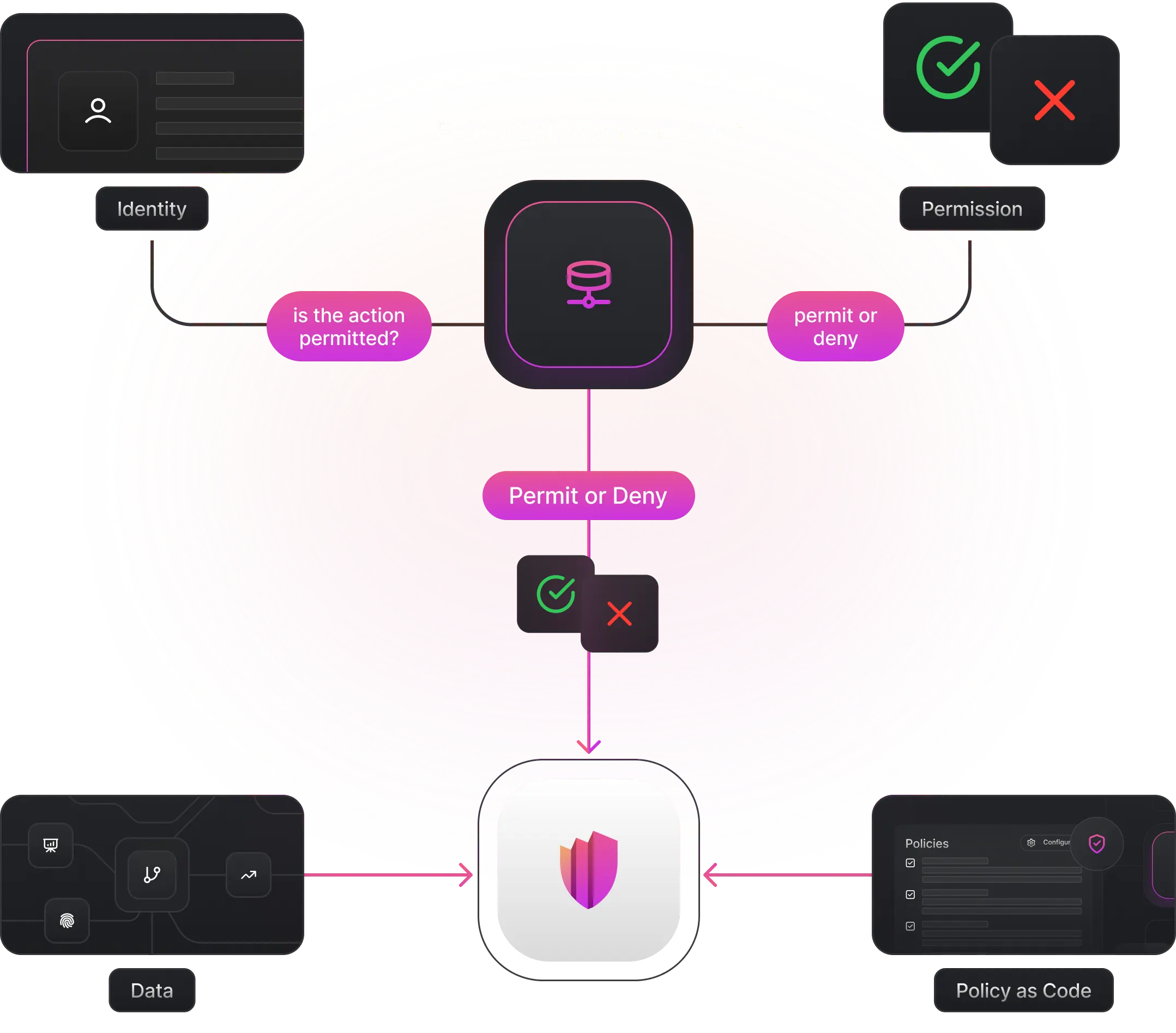
The same policy model is applied across all enforcement layers, ensuring authorization remains:
- governed in intent — rules are collaboratively reviewed, versioned, and managed
- decentralized in enforcement — decisions occur close to where actions happen
- auditable and explainable — full end-to-end visibility across the authorization path
Centralized Interface, Evolving Toward Decentralized Consensus
Policies are accessed through a unified control-plane interface, but this does not imply a centralized trust model.
- The current implementation runs through a single, centralized access point for operational simplicity.
- However, the underlying architecture and algorithms are already designed to be extended with decentralized consensus behind that interface.
Enforcement remains fully distributed, while the control-plane provides a consistent place to define, review, update, and audit policies — even as the system evolves toward decentralized trust models.
Permguard offers strong Zero Trust security with a simple integration path — define authorization intent once and enforce it everywhere.
Bring Your Own Identity (BYOI)
Permguard is identity-agnostic on the authentication side.
It follows a Bring Your Own Identity (BYOI) approach:
- it consumes any identity your system already provides
- it supports both user and workload identities
- it does not replace your existing AuthN layer
The main goal of Permguard is to provide strong authorization with built-in trust governance, not authentication.
Where Authorization Runs
Authorization can be triggered by either:
Network Layer e.g., service mesh, sidecar proxy, gateway, or edge component.
Application Layer via SDKs or native APIs.
In both cases, the request is always evaluated before performing any action.
Each incoming request carries at least two identities:
- Self identity — the workload performing the action
- Peer identity — the caller (user or workload)
Additional attestations may also be included, such as tokens, workload proofs, or signed claims.
The data-plane receives the full request context (identities, attestations, network metadata, application attributes) and evaluates it locally using policies obtained from the control-plane.
- The control-plane manages and distributes policies
- The data-plane enforces permit/deny decisions at the workload boundary
This creates a consistent and decentralized Zero Trust model for both synchronous and asynchronous workflows.
Designed for cloud-native, edge, and multi-tenant environments, Permguard enables updating policies without changing application code.
Policy Languages
Permguard is language-agnostic and supports multiple policy languages, starting with Cedar:
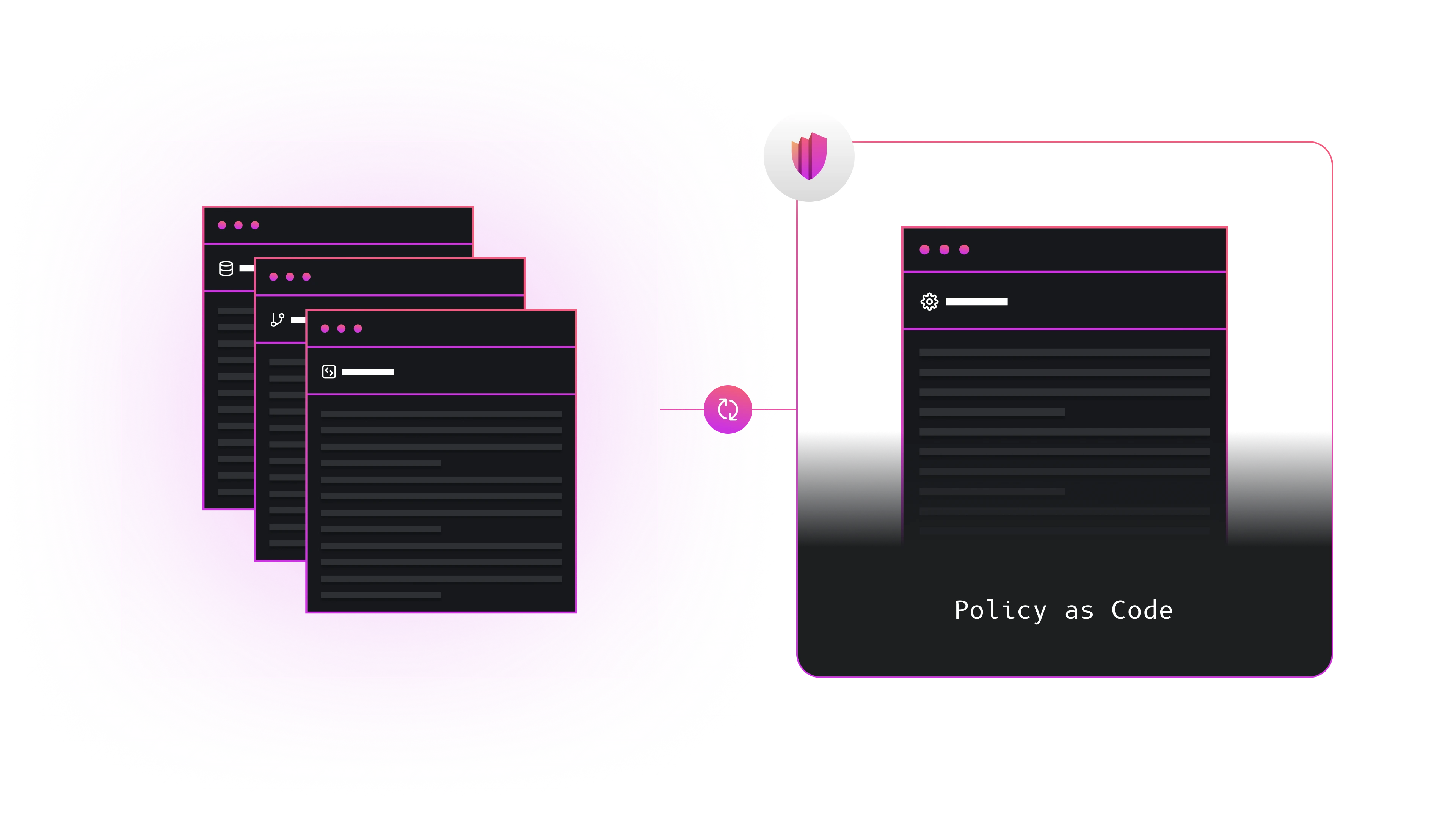
Each language is implemented through a thin abstraction layer that keeps the core model stable while requiring only a minimal common keyword set.
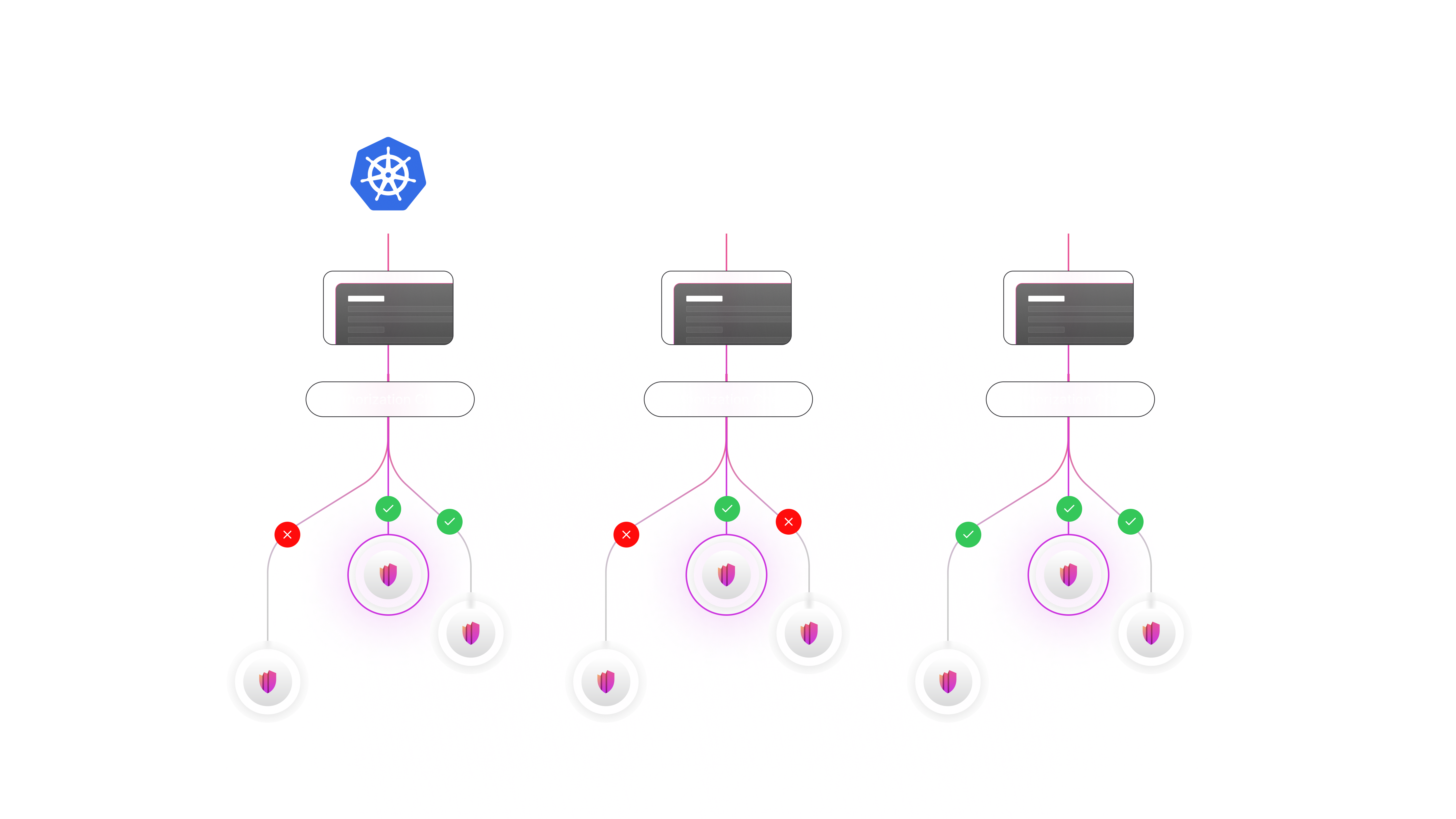
Deployment Flexibility
Permguard can run in:
on-premises,private, orpubliccloud environmentsKubernetesandserverlessplatformsedgeandIoTecosystems, includingpartially connectedordisconnectedscenarios
The architecture consists of two main components:
Control PlaneMust be reachable at the network level to expose policy governance. It can also run onedgecomponents or distributed infrastructure as long as it provides a consistent governance view.Data PlanesCan be deployed anywhere — inside applications, gateways, edge devices, remote regions, or disconnected environments.
Integrating with Permguard
Applications can enforce access control using:
- the official SDKs, or
- Permguard’s native APIs
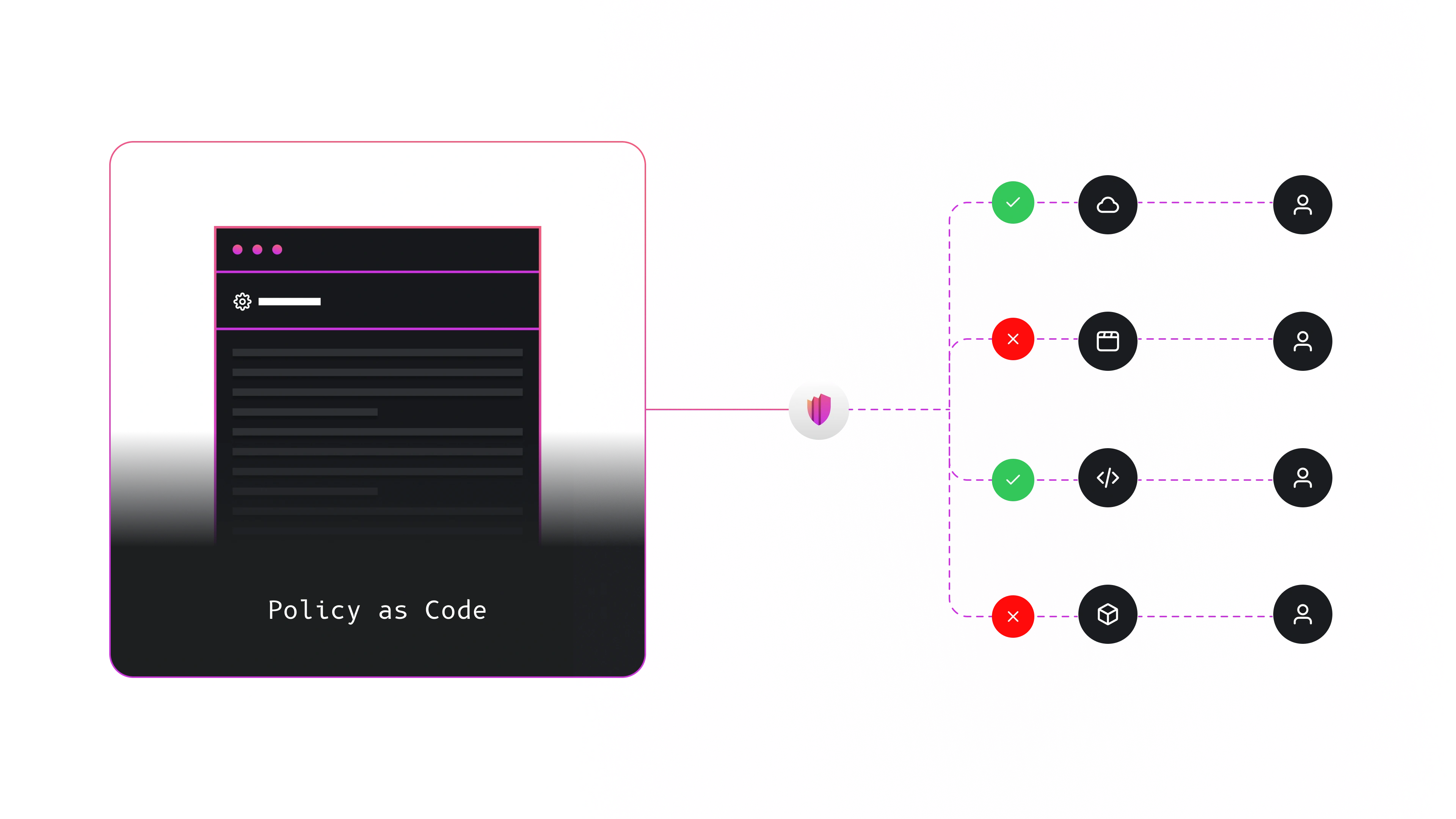
SDKs are available for Go, Rust, Java, .NET Core, Node.js, and Python, with more in development.
Summary
Permguard provides:
- Strong Zero Trust authorization
- Distributed enforcement
- Centralized governance of intent
- Integration at network or application layers
- Support for multiple identity systems
- Language-agnostic policy definitions
- Flexible deployment across clouds, edge, and IoT
Together, these capabilities provide precise control over who can access which resources, with consistent security across heterogeneous environments.

